First-in human(FIH) studies required to assess the safety of new investigational products often encounter mild to severe adverse responses that are immune-mediated, despite completing all required pre-clinical safety and toxicology studies in animals.
At GBS Leiden we strive to provide the most relevant models for in vitro evaluation of immunotoxicity.
We offer a dedicated suite of biomarkers based on actual case studies of immunotoxic compounds that captures the most common problems encountered during Phase I studies. Our experience ranges from E.coli and mammalian derived biologicals to small molecules. Our ultra-clean workflows minimize background reactions and allows us to achieve the most sensitive detection limits. Evaluation of your investigational new compound in Xvi-Blood or PBMCs assay as well as plasma aids in troubleshooting the source of the reaction, and provides indications for potential contaminants, without risk to human subjects.
APPLICATIONS:
- ● Evaluate new manufacturing or purification methods
- ● Troubleshooting for FIH trials, including in vivo confirmation of circulating biomarkers
- ● Asses the risks to target population with potential for increased susceptibility of immunotoxic responses

We can deliver interim data reports with rapid turnaround times to support safety monitoring during FIH.
EXAMPLE DATA
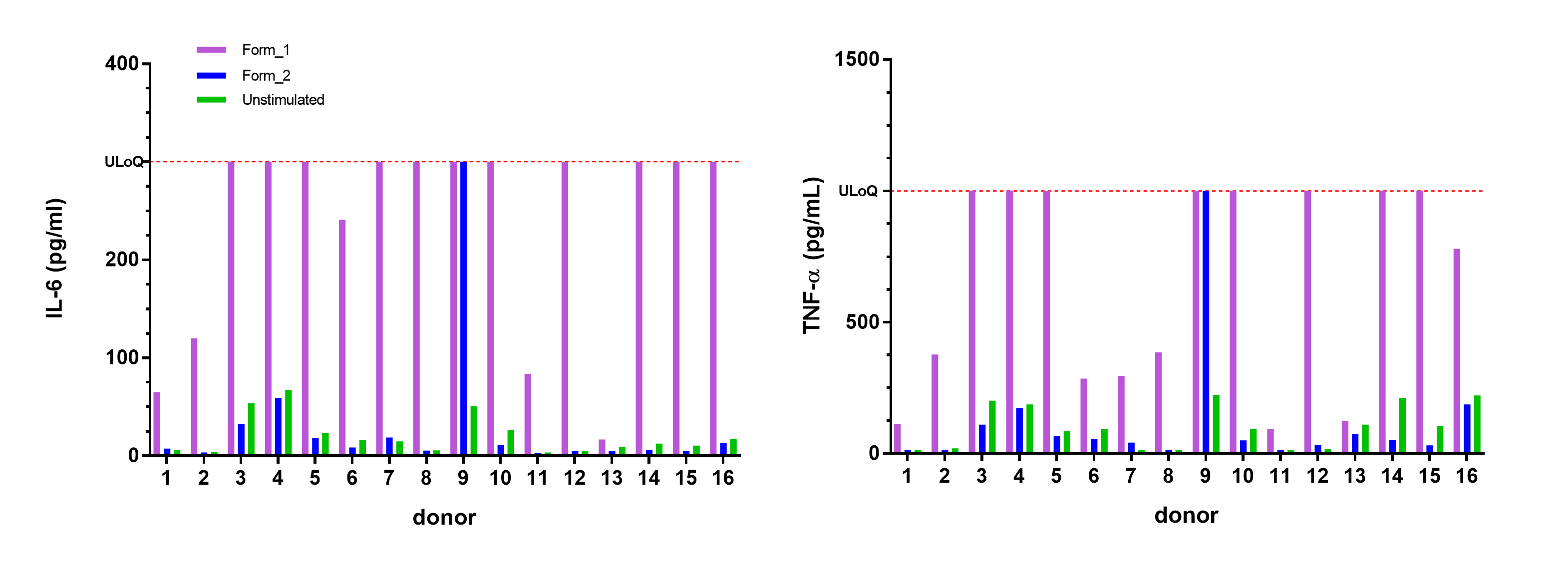
Figure: Assessment of immunotoxic potential of a new drug produced using two different purification procedures in Xvi-Blood assay.
Formulation 1 (Form_1) exhibits undesired robust immune cell activation compared to Formulation 2 (Form_2) as evaluated by IL-6 and TNF-α levels in supernatants after 4h incubation. ULoQ stands for upper limit of quantification.
EXAMPLE DATA
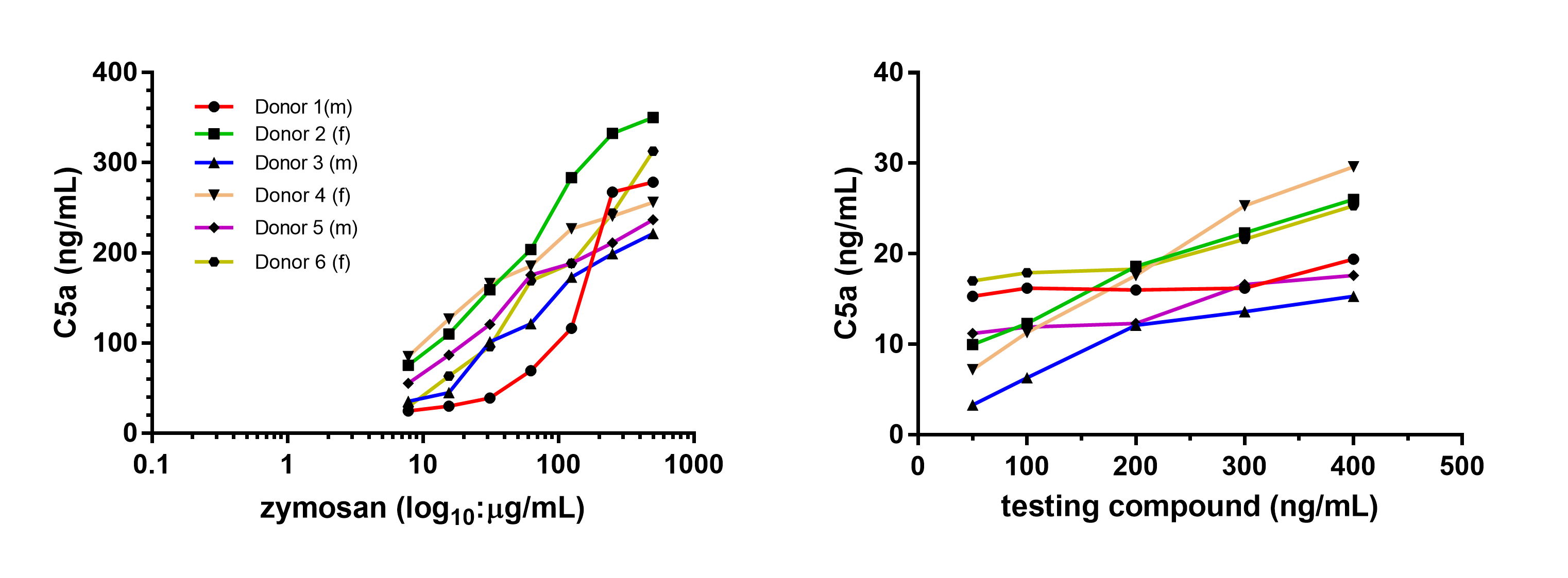

Figure: Assessment of complement activation potential of new drug.
Complement activation (C5a) was measured in the supernatants after application of serial dilutions of either of zymosan (positive control) or tested compound in Xvi-Blood assay. The tested compound exhibits low levels of C5a over wide range of serial dilutions indicating that the compound rather possess low potential for contact activation.
